Structural compressibility in 3d printed abrasion protection structures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25367/cdatp.2020.1.p3-11Keywords:
textiles, 3D printing, functionalization, abrasion, compressibilityAbstract
Abrasion protection in exposed areas is a common method of extending the life cycle of textile products. To achieve sufficient abrasion resistance, the textile products are usually coated or partially printed with hard products. But hard materials lead to stiffening and can have a negative effect on the haptics.
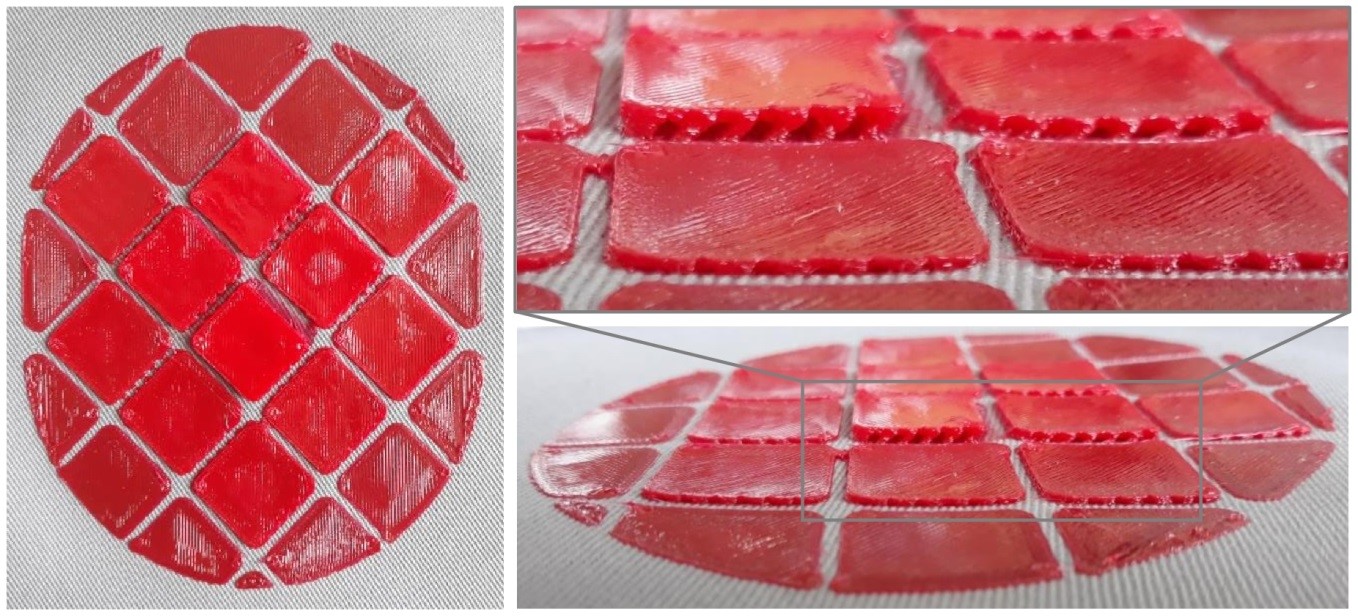
The aim of this study is the application of abrasion-resistant and compressible print patterns directly to textile substrates by 3D printing. The compressibility is achieved by the inner structure, which, in contrast to conventional coatings, is not 100 % filled. In the investigations, four thermoplastic materials were tested for their abrasion resistance and compressible properties. Fabrics made of cotton or polyester/cotton blends were used as textile substrates. Different approaches were taken to create the structures, some of which can only be realized using 3D printing technology.
The abrasion resistance of the substrates could be increased from 50 abrasion cycles to over 8,000 cycles with the help of the 3D printed patterns. It was possible to print 3D structures that could be compressed in thickness by up to 53 %. The combination of both properties, abrasion resistance and compressibility, can be used for new types of individual products with good wearing comfort and functionality that meet the requirements, especially in the areas of functional, protective and sports clothing.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Sarah Lysann Göbel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





